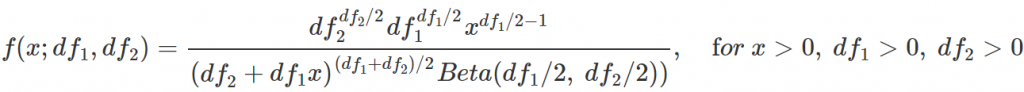
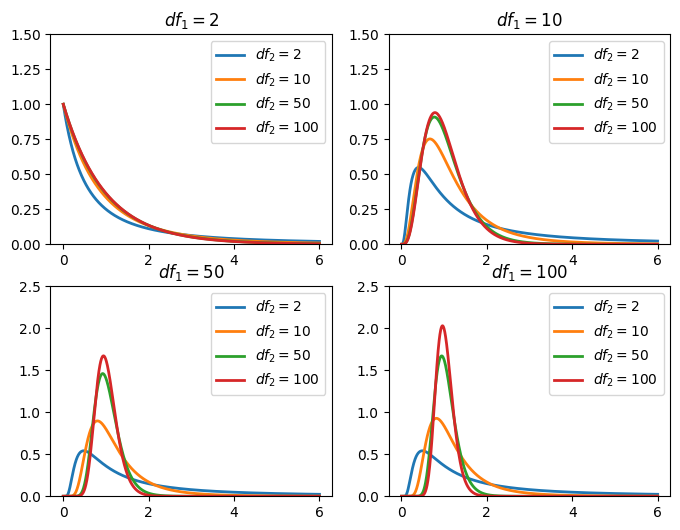
F 分配在 Python 的 PDF 程式代碼為 f.pdf ,其程式所使用的 PDF 如上,函數共具 2 個不同的參數 $df_1$ 與 $df_2$,函數的形狀由此些參數決定。如下圖,可以看出:
# F distribution
from scipy.stats import f
xlim_f = [0, 6]
x_diff_f = np.linspace(xlim_f[0], xlim_f[1], 10000)
color = np.array(['red', 'orange', 'yellow', 'green'])
# fig1
df1 = 2
df2 = np.array([2, 10, 50, 100])
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=[8, 6])
for i in df2:
Y = f.pdf(x_diff_f, df1, i)
ax[0][0].plot(x_diff_f, Y, linewidth=2, #color=color[i], \
label=r'$df_2 = {}$'.format(i))
ax[0][0].legend()
ax[0][0].grid(False)
ax[0][0].set_ylim([0, 1.5])
ax[0][0].set_title(r'$df_1 = 2$')
# fig2
df1 = 10
df2 = np.array([2, 10, 50, 100])
for i in df2:
Y = f.pdf(x_diff_f, df1, i)
ax[0][1].plot(x_diff_f, Y, linewidth=2, #color=color[i], \
label=r'$df_2 = {}$'.format(i))
ax[0][1].legend()
ax[0][1].grid(False)
ax[0][1].set_ylim([0, 1.5])
ax[0][1].set_title(r'$df_1 = 10$')
# fig3
df1 = 50
df2 = np.array([2, 10, 50, 100])
for i in df2:
Y = f.pdf(x_diff_f, df1, i)
ax[1][0].plot(x_diff_f, Y, linewidth=2, #color=color[i], \
label=r'$df_2 = {}$'.format(i))
ax[1][0].legend()
ax[1][0].grid(False)
ax[1][0].set_ylim([0, 2.5])
ax[1][0].set_title(r'$df_1 = 50$')
# fig4
df1 = 100
df2 = np.array([2, 10, 50, 100])
for i in df2:
Y = f.pdf(x_diff_f, df1, i)
ax[1][1].plot(x_diff_f, Y, linewidth=2, #color=color[i], \
label=r'$df_2 = {}$'.format(i))
ax[1][1].legend()
ax[1][1].grid(False)
ax[1][1].set_ylim([0, 2.5])
ax[1][1].set_title(r'$df_1 = 100$')
plt.show()
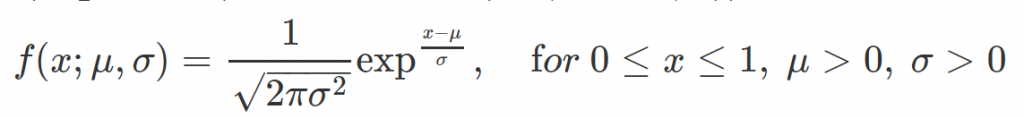
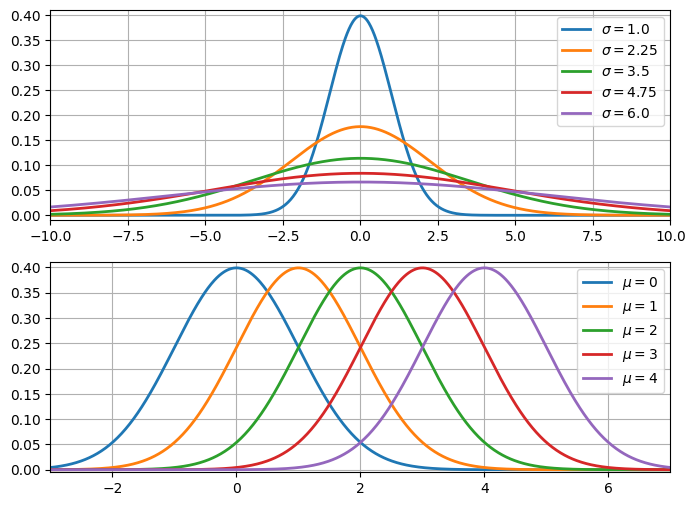
Normal 分配的 PDF 在 Python 中的程式碼為 norm.pdf ,其程式所依據的 PDF 如上式。設定不同的參數 $\mu$ 與 $\sigma$ 之下,如下圖,可觀察到隨 $\sigma$ 增大,PDF 越呈厚尾,其峰度也越小。而當 $\sigma$ 固定,隨 $\mu$ 變動,PDF 對稱的中軸線也隨之平移,但曲線的形狀(峰度與偏度)沒有改變。
# Normal distribution
from scipy.stats import norm
# sigma = np.linspace(1, 5+1, 1)
# mu = np.linspace(0, 4+1, 4)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=[8, 6], squeeze=False)
# fig1 -- different sigma
xlim = [-10., 10.]
x_diff_normal_scale = np.linspace(xlim[0], xlim[1], 1000)
mu = 0
sigma = np.linspace(1, 5+1, 5)
for i in sigma:
Y = norm.pdf(x_diff_normal_scale, loc=mu, scale=i)
ax[0][0].plot(x_diff_normal_scale, Y, linewidth=2, \
label=r'$\sigma = {}$'.format(i))
ax[0][0].set_xticks(np.arange(xlim[0], xlim[1]+2.5, 2.5))
ax[0][0].set_xlim(xlim)
ax[0][0].set_yticks(np.arange(0, 0.4+0.05, 0.05))
ax[0][0].set_ylim(0-0.01, 0.4+0.01)
ax[0][0].grid(True)
ax[0][0].legend()
# fig2 -- different mu
xlim = [-4., 9]
x_diff_normal_location = np.linspace(xlim[0], xlim[1], 1000)
mu = np.linspace(0, 4, 5, dtype=int)
sigma = 1
for i in mu:
Y = norm.pdf(x_diff_normal_location, loc=i, scale=sigma)
ax[1][0].plot(x_diff_normal_location, Y, linewidth=2, \
label=r'$\mu = {}$'.format(i))
ax[1][0].set_xticks(np.arange(xlim[0], xlim[1]+2, 2))
ax[1][0].set_xlim(-3, 7)
ax[1][0].set_yticks(np.arange(0, 0.4+0.05, 0.05))
ax[1][0].set_ylim(0-0.005, 0.4+0.01)
ax[1][0].grid(True)
ax[1][0].legend()
plt.show()
連續型的機率分配介紹到這裡結束,下篇開始介紹離散型分配,分配包含:Negative Binomial、Geometric、Hypergeometric。
